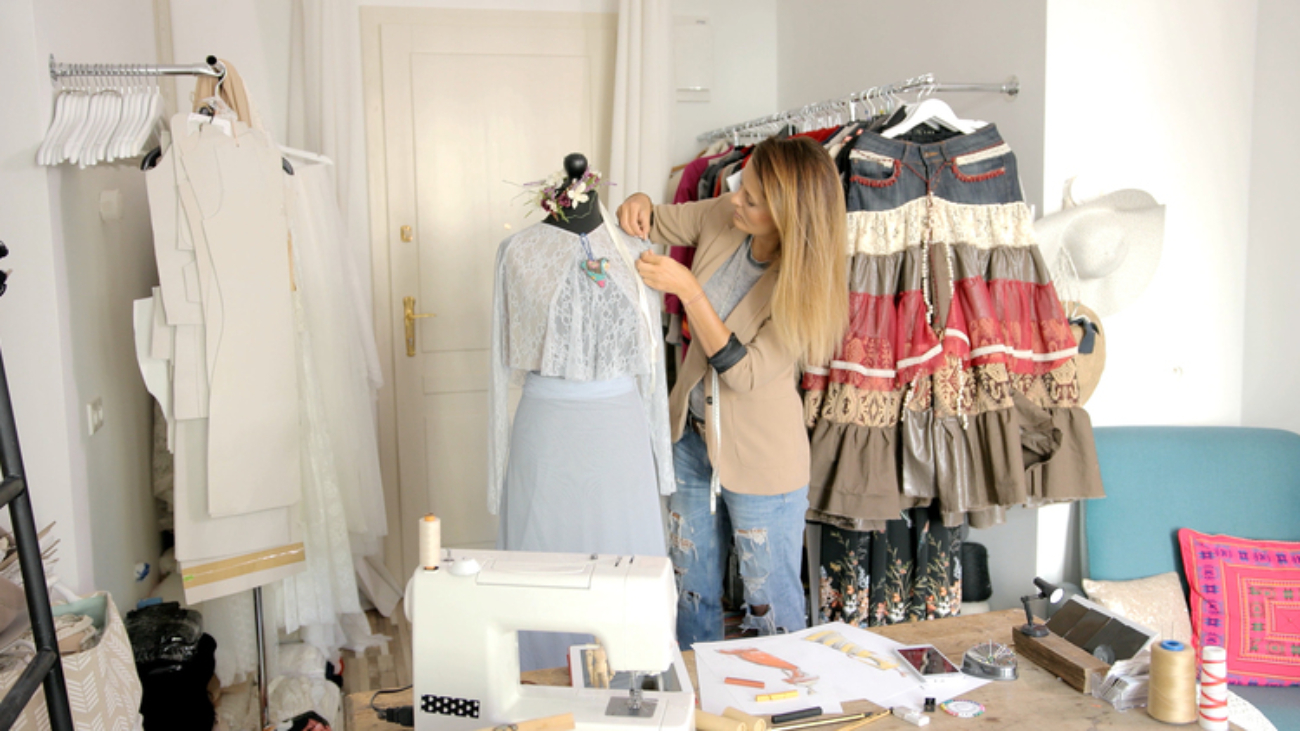
13. Staying Relevant and Evolving in the Industry
Staying relevant and evolving in any industry means continuously adapting to changes, learning new skills, and staying connected to trends and consumer needs. It ensures longevity and success in a competitive market.
Keeping Up with Industry Changes
The fashion industry evolves rapidly, with new trends, technologies, and consumer demands shaping its landscape. Staying updated is essential for success. Here are some ways to keep up with industry changes:
1. Follow Fashion Weeks and Trade Shows
- Stay updated with major fashion events like Paris, Milan, New York, and London Fashion Weeks.
- Attend trade shows such as Première Vision, MAGIC, or Pitti Uomo to discover new fabrics, materials, and innovations.
2. Read Fashion Publications and Websites
- Follow industry-leading publications like Vogue, Business of Fashion, WWD, Elle, and Harper’s Bazaar.
- Explore trend forecasting platforms like WGSN and Fashion Snoops.
3. Engage with Fashion Communities and Networks
- Join online and offline fashion communities to discuss trends and innovations.
- Attend industry networking events, workshops, and designer panels.
4. Keep an Eye on Social Media and Influencers
- Follow fashion influencers, stylists, and designers on Instagram, TikTok, and Pinterest.
- Analyze how digital creators impact fashion trends and consumer behavior.
5. Study Emerging Technologies
- Learn about AI-driven design, 3D printing, virtual fashion, and digital clothing.
- Explore tools like Clo 3D, Adobe Substance, and blockchain applications in fashion.
6. Observe Consumer Behavior and Market Shifts
- Pay attention to how consumers are shopping—sustainability, inclusivity, and ethical fashion are growing trends.
- Monitor e-commerce trends and the rise of direct-to-consumer brands.
7. Experiment with New Design Techniques
- Stay ahead by learning about upcycled fashion, smart textiles, and alternative materials.
- Adapt to industry shifts by integrating eco-friendly and tech-driven processes.
8. Take Continuous Learning Seriously
- Enroll in online courses, attend workshops, and learn new skills in fashion business, digital design, or marketing.
- Follow thought leaders and participate in discussions about the future of fashion.
Adapting to New Technologies and Trends
The fashion industry is constantly evolving, and staying ahead requires embracing new technologies and trends.
1. Embracing Digital Tools & Innovation
- Use 3D design software like CLO3D and Browzwear for virtual prototyping.
- Implement AI-driven fashion forecasting for trend predictions.
- Explore NFTs and digital fashion in the metaverse.
2. Staying Updated on Trends
- Follow fashion weeks, trade shows, and industry reports.
- Monitor consumer behavior, sustainability movements, and cultural shifts.
- Engage with social media, influencers, and emerging brands.
3. Sustainable & Smart Fashion
- Experiment with eco-friendly materials, zero-waste design, and circular fashion.
- Incorporate smart textiles and wearable technology.
4. E-Commerce & Marketing Adaptation
- Optimize online presence with AR fitting rooms, AI chatbots, and data-driven marketing.
- Leverage social commerce, live shopping, and influencer collaborations.
Experimenting with New Materials and Techniques
Innovation in materials and techniques can elevate your designs, increase sustainability, and set you apart in a competitive industry. Here’s how to explore new possibilities:
1. Sustainable & Eco-Friendly Materials
- Recycled fabrics (e.g., recycled polyester, upcycled denim).
- Plant-based fabrics (e.g., hemp, Tencel, Piñatex from pineapple fibers).
- Biodegradable textiles (e.g., mushroom leather, algae-based fabrics).
2. Advanced Technology in Fabrics
- Smart textiles: Incorporate fabrics that change color, adapt to temperature, or monitor health.
- 3D-knitting: Create seamless, custom-fit designs directly from digital patterns.
- Conductive fabrics: Integrate electronics for wearable tech applications.
3. Innovative Construction Techniques
- Zero-waste pattern making: Use every inch of fabric, eliminating waste.
- 3D printing: Create intricate, customized designs and accessories using printed materials.
- Laser cutting: Add precision and detail to garments and accessories.
4. Mixed Media & Multi-Sensory Designs
- Combine unexpected materials like metal, rubber, and fabric to create unique textures and looks.
- Explore sound and light effects for interactive fashion pieces.
Experimenting with new materials and techniques keeps your designs fresh, sustainable, and forward-thinking while allowing you to stand out in an ever-evolving industry.
The Impacts of Technology in Fashion Design
Technology has drastically transformed the fashion industry, offering new tools and opportunities for designers. Here’s how it has made an impact:
1. Digital Design & Prototyping
- CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and 3D design software (e.g., CLO3D, Browzwear) allow designers to create detailed digital garments, reducing the need for physical prototypes.
- Virtual sampling and 3D printing enable rapid iteration, saving time and materials.
2. Advanced Fabric Technologies
- Smart textiles and wearable tech are changing the way fashion interacts with the body, offering features like temperature control or health monitoring.
- Sustainable fabric innovations: Using technologies to create recycled materials, bio-fabrics, and eco-friendly dyes to reduce the environmental impact.
3. Manufacturing & Production
- Automation and robotics streamline garment production, increasing efficiency and precision.
- 3D knitting machines allow for customized, on-demand garment production, minimizing waste.
4. Data-Driven Design
- AI and machine learning are used to predict trends, understand consumer preferences, and optimize product development.
- Virtual fitting rooms and augmented reality (AR) help customers visualize designs before purchase, enhancing the shopping experience.
5. E-Commerce & Marketing
- Social media platforms and AI-powered ads allow designers to market directly to consumers, enhancing brand visibility.
- Data analytics guide marketing strategies, helping brands understand what resonates with their audience.
AI and 3D Printing in Fashion
AI in Fashion:
- Design Innovation – AI-powered design tools analyze trends, consumer preferences, and historical data to generate new fashion concepts. Brands like H&M and Zalando use AI for predictive design.
- Personalized Shopping – AI-driven recommendation engines suggest clothing based on users’ preferences, sizes, and past purchases (e.g., Amazon’s AI styling services).
- Smart Textiles & Wearables – AI enhances textiles with features like temperature control, biometric sensing, and self-cleaning materials.
- Supply Chain Optimization – AI improves inventory management, demand forecasting, and logistics to reduce waste.
- Virtual Try-On & Fitting – AI-based AR solutions (e.g., Zara’s AR app, Snapchat filters) allow customers to visualize outfits before purchase.
3D Printing in Fashion:
- Sustainable Production – 3D printing reduces fabric waste, as materials are printed layer by layer instead of cut from larger pieces.
- Customization & On-Demand Fashion – Brands like Adidas (Futurecraft 4D), Iris van Herpen, and Balenciaga use 3D printing to create personalized designs and footwear.
- Complex & Unique Designs – Designers can create intricate, avant-garde pieces that would be impossible with traditional sewing techniques.
- Eco-Friendly Materials – 3D printing uses biodegradable, recycled, and plant-based materials to promote sustainability.
- Fast Prototyping – Reduces the time and cost of producing prototypes and samples, speeding up the design process.
Virtual Fashion Shows and Digital Avatars
Virtual Fashion Shows:
- Immersive Experiences – Brands like Balenciaga, Gucci, and Prada have used virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and the metaverse to host digital runway shows.
- Cost & Sustainability Benefits – Digital shows eliminate travel and production waste, making fashion more eco-friendly.
- Wider Accessibility – Viewers worldwide can attend fashion shows without geographical restrictions.
- Interactive Elements – Some brands incorporate NFTs, AR try-ons, and gamification to engage audiences.
Digital Avatars in Fashion:
- Virtual Models – AI-powered models like Lil Miquela and Shudu Gram are redefining brand campaigns.
- Customizable Avatars – Platforms like Zepeto and Ready Player Me allow users to dress avatars in designer wear.
- Metaverse Fashion – Digital outfits (NFT wearables) are sold on platforms like Decentraland and The Sandbox.
- AI-Powered Personalization – Avatars can model custom outfits, allowing brands to create hyper-personalized shopping experiences.
14. Case Studies: Success Stories of Fashion Designers
Here are some success stories of well known fashion designers that have become known all over the world.
Coco Chanel: Reinventing Women’s Fashion
Gabrielle “Coco” Chanel was a revolutionary fashion designer who redefined women’s fashion in the early 20th century. She challenged the restrictive clothing norms of the time, introducing comfortable, elegant, and functional designs. Her innovations shaped modern fashion, making her one of the most influential designers in history.
Chanel’s Innovations & Reinvention of Women’s Fashion
1. Introduction of Comfortable & Functional Fashion
- Replaced stiff corsets with looser, androgynous silhouettes.
- Introduced jersey fabric, traditionally used for men’s underwear, into women’s fashion for comfort and flexibility.
- Created sportswear-inspired fashion, allowing freedom of movement for active women.
2. The Little Black Dress (LBD) – 1926
- Revolutionized the concept of simplicity and elegance with the LBD.
- Prior to Chanel, black was reserved for mourning, but she transformed it into a symbol of timeless sophistication.
- Vogue called it the “Ford of fashion,” highlighting its universal appeal.
3. The Chanel Suit – 1925
- Designed a collarless tweed suit with a knee-length skirt and a fitted jacket, giving women a chic yet professional look.
- Inspired by menswear, it symbolized female empowerment and independence.
- Became a favorite of icons like Jackie Kennedy and Princess Diana.
4. Chanel No. 5 Perfume (1921)
- First-ever designer fragrance with a complex, sophisticated floral scent.
- Revolutionized perfume marketing by associating a scent with luxury and femininity.
- Marilyn Monroe famously stated she wore “nothing but Chanel No. 5 to bed.”
5. Costume Jewelry & Accessories
- Challenged the norm that jewelry had to be expensive by introducing fashion jewelry made of faux pearls and gold plating.
- Made accessorizing fashionable for women of all classes.
Impact on Fashion & Society
1. Breaking Gender Norms
- Popularized trousers for women, encouraging gender-fluid dressing.
- Made short haircuts fashionable, challenging traditional feminine beauty standards.
2. Democratizing Luxury
- Made high fashion more accessible and wearable compared to the extravagant couture of previous decades.
- Proved that elegance doesn’t need excessive decoration but rather good design and tailoring.
3. Enduring Legacy & Influence on Modern Designers
- Chanel’s minimalist and timeless approach inspired designers like Yves Saint Laurent, Karl Lagerfeld, and Phoebe Philo.
- The Chanel brand remains a global fashion powerhouse, constantly evolving while staying true to Coco’s vision.
Virgil Abloh: Blending Streetwear with Luxury
Virgil Abloh (1980–2021) revolutionized fashion by seamlessly merging streetwear aesthetics with high-end luxury. As the founder of Off-White and the first Black artistic director of Louis Vuitton’s menswear, Abloh disrupted traditional fashion hierarchies and redefined modern luxury.
Defining the Streetwear-Luxury Crossover
Off-White: High-End Streetwear:
- Luxury-Level Craftsmanship: Unlike typical streetwear brands, Off-White used premium materials and Italian tailoring.
- Cultural References: Integrated elements from hip-hop, skate culture, and art, making fashion more relatable to younger audiences.
- “Elevated Basics”: Items like hoodies and sneakers were reimagined with deconstruction, irony, and unique branding.
Louis Vuitton (2018–2021): Streetwear in a Heritage Brand:
- First Collection (Spring/Summer 2019): Blended streetwear silhouettes (baggy pants, utility vests) with luxury fabrics.
- Diversity & Inclusion: Cast models from diverse backgrounds and celebrated Black culture in high fashion.
- Iconic Pieces:
- LV Trainer Sneaker: Inspired by vintage basketball shoes, merging hype culture with luxury.
- Soft Trunk Bags: Transformed traditional LV luggage into modern, crossbody accessories.
- Rainbow Gradient: Symbolizing inclusivity and optimism, seen in his debut LV collection.
Key Collaborations
Nike x Off-White (“The Ten”):
- Deconstructed classic Nike silhouettes (e.g., Air Jordan 1, Air Presto, Air Force 1).
- Mixed industrial elements (zip ties, exposed foam) with storytelling, creating resale hype.
IKEA x Virgil Abloh:
- Designed affordable, fashion-forward home decor pieces.
- The “KEEP OFF” rug became a cultural statement, merging streetwear with interiors.
Mercedes-Benz x Virgil Abloh:
- Reimagined the G-Class into a futuristic, off-road concept, blending automotive luxury with street aesthetics.
Legacy & Impact
- Breaking Industry Barriers: First Black artistic director at a major luxury house.
- Hypebeast Meets Haute Couture: Proved that streetwear could be high fashion.
- Cultural Visionary: Pioneered fashion x music x art collaborations, influencing designers like Matthew Williams (Givenchy) and Samuel Ross (A-COLD-WALL*).
- Final LV Show (2021): “Virgil Was Here” collection celebrated his vision of democratized fashion.
Stella McCartney: Leading Sustainable Fashion
Stella McCartney is a pioneering fashion designer known for her commitment to sustainable and cruelty-free fashion. Since launching her brand in 2001, she has revolutionized the industry by proving that high fashion and sustainability can coexist. Through innovation, ethical sourcing, and environmental consciousness, McCartney has set a benchmark for responsible luxury fashion.
Stella McCartney’s Sustainable Strategies
1. Cruelty-Free & Vegan Fashion
- No leather, fur, or exotic skins used in collections—a groundbreaking move in luxury fashion.
- Developed vegan leather alternatives made from plant-based materials and recycled plastics.
- Partnered with Bolt Threads to develop Mylo™, a leather alternative made from mushroom roots.
2. Ethical Sourcing & Materials Innovation
- Uses organic cotton, recycled polyester, and regenerated cashmere to reduce environmental impact.
- Collaborated with Econyl®, a company that transforms ocean plastic and waste into regenerated nylon.
- Introduced KOBA® faux fur, made from plant-based and recycled fibers, to offer sustainable luxury.
3. Circular Fashion & Waste Reduction
- Advocates for a circular economy—designing clothes for longevity and recyclability.
- Launched the “World’s First Fully Circular Hoodie” with Adidas, made from organic cotton and recycled materials.
- Encourages customers to repair, resell, and recycle garments instead of discarding them.
4. Carbon Footprint Reduction
- Uses renewable energy in production facilities.
- Implements zero-waste policies in factories and retail spaces.
- Developed Air Dyeing Technology, which reduces water and energy consumption in fabric dyeing.
5. Transparency & Industry Influence
- Published sustainability reports to educate consumers and push for industry-wide change.
- Partnered with LVMH in 2019 to scale sustainable luxury fashion globally.
- Works with organizations like the Ellen MacArthur Foundation to promote circular fashion initiatives.
Impact on Fashion & Society
1. Changing Industry Norms
- Proved that sustainable fashion can be profitable, influencing luxury brands like Gucci, Burberry, and Prada to adopt ethical practices.
- Helped normalize vegan fashion—a once niche market now growing rapidly.
2. Raising Consumer Awareness
- Educated consumers on the environmental impact of fashion, encouraging ethical purchasing decisions.
- Pioneered sustainability-focused marketing campaigns, making eco-friendly fashion desirable.
3. Expanding Sustainable Fashion Beyond Clothing
- Designed sustainable sportswear in collaboration with Adidas.
- Created eco-friendly skincare and accessories, proving sustainability extends beyond apparel.
15. Conclusion: Your Journey as a Fashion Designer
Your journey as a fashion designer is a continuous path of creativity, learning, and growth. From overcoming challenges to refining your skills and finding your unique style, each step shapes your career. Embracing both successes and setbacks helps you evolve as a designer, pushing you to innovate and stay true to your vision. Whether working for a brand or building your own, the journey is about staying passionate, adaptable, and dedicated to creating meaningful, impactful designs. Ultimately, it’s a blend of persistence, creativity, and resilience that defines your success in the fashion industry.
The Importance of Lifelong Learning
Lifelong learning is essential for personal and professional growth in a rapidly changing world. It allows individuals to stay relevant, adapt to new challenges, and enhance their knowledge continuously.
Key Points:
- Adaptability: In a fast-evolving job market, continuous learning helps individuals keep up with new trends and technologies.
- Personal Growth: Expands perspectives, improves cognitive abilities, and fosters creativity.
- Career Advancement: Enhances skills and qualifications, increasing job opportunities and earning potential.
- Self-Confidence: Knowledge empowers individuals to take on new challenges with confidence.
Embracing New Skills and Innovations
Adopting new skills and staying updated with innovations is crucial in a competitive and technology-driven world. It ensures efficiency, enhances problem-solving abilities, and opens new opportunities.
Key Points:
- Staying Relevant: Learning new technologies and methodologies keeps individuals competitive in their fields.
- Increased Productivity: Automation and digital tools streamline processes, improving efficiency.
- Innovation & Creativity: Exposure to new ideas fosters innovation and unique problem-solving approaches.
- Career Flexibility: Enables professionals to transition into new roles or industries with ease.
Continuous Improvement Through Experience
Experience is a powerful teacher, and continuous improvement through reflection and practice leads to mastery in any field. Learning from past mistakes and successes ensures steady personal and professional growth.
Key Points:
- Learning from Failure: Mistakes provide valuable lessons that contribute to better decision-making.
- Developing Expertise: Regular practice and refinement lead to skill mastery.
- Adapting to Change: Experience helps individuals anticipate challenges and respond effectively.
- Enhancing Problem-Solving Skills: Real-world exposure sharpens analytical thinking and decision-making abilities.
Staying True to Your Vision and Passion
In any creative industry, especially fashion, staying true to your vision and passion is crucial for long-term success. While trends come and go, a strong personal vision ensures authenticity and sets a designer apart from the competition.
Key Points:
- Authenticity Wins: Consumers and industry professionals appreciate designers who create from the heart rather than follow fleeting trends.
- Resilience & Motivation: Passion fuels perseverance, helping designers push through challenges and setbacks.
- Legacy & Influence: Staying true to a vision helps create a lasting impact, making a designer’s work timeless.
- Connection with Audience: A clear vision attracts like-minded customers who resonate with the brand’s message and aesthetic.
Building a Unique Identity in a Crowded Market
With countless fashion brands competing for attention, establishing a unique identity is essential for standing out. A strong brand identity not only attracts customers but also builds long-term loyalty.
Key Points:
- Signature Style: Developing a recognizable aesthetic—whether through fabric choices, silhouettes, or craftsmanship—makes a brand memorable.
- Brand Storytelling: Sharing a compelling backstory and mission helps consumers connect emotionally with the brand.
- Innovation & Differentiation: Experimenting with materials, sustainability, and cultural influences can help a brand carve its niche.
- Consistency Across Platforms: From runway shows to social media, maintaining a cohesive brand image strengthens market presence.
Impacting the Fashion Industry with Your Designs
Fashion is more than just clothing—it’s a powerful tool for cultural expression, sustainability, and social change. Designers who bring fresh perspectives and purpose-driven innovation can leave a significant mark on the industry.
Key Points:
- Sustainability & Ethics: Implementing eco-friendly materials and ethical production practices can set a brand apart and influence industry standards.
- Empowering Messages: Using fashion to make statements on gender, diversity, or inclusivity can drive societal change.
- Technological Advancements: Integrating AI, 3D printing, or smart textiles can push the boundaries of design.
- Inspiring Future Designers: Success and innovation can inspire upcoming talents to pursue their own creative journeys.
16. Additional Resources for Aspiring Fashion Designers
Here are some different additional resources because it’s always good to get more knowledge.
Books and Magazines on Fashion Design
Here are some examples of books about fashion design and go to magazines for anyone interested in fashion.
- “The Fashion System” – Roland Barthes – A deep dive into how fashion communicates through signs and symbols.
- “Patternmaking for Fashion Design” – Helen Joseph-Armstrong – A must-have for understanding garment construction and pattern creation.
- “Fashion Design Essentials” – Jay Calderin – Covers key principles in design, color theory, and garment structure.
- “Dior by Dior” – Christian Dior – A memoir detailing Dior’s creative process and rise in the industry.
- Vogue – The go-to for high fashion, trends, and designer interviews.
- Harper’s Bazaar – Covers both classic elegance and avant-garde styles.
- Elle – A mix of fashion, beauty, and lifestyle.
- i-D – Youth-driven fashion with a focus on edgy and alternative styles.
- Dazed – Explores experimental fashion and emerging designers.
Online Courses and Fashion Schools
Here are some online courses you can take as part of your self-taught journey. Also worldwide known fashion schools that may interest you.
Online Fashion Courses
- Coursera: Fashion as Design (MoMA)
- FutureLearn: Fashion and Sustainability (LCF)
- Udemy: Fashion Design for Beginners
- MasterClass: Fashion Design by Marc Jacobs
- Domestika: Introduction to Fashion Design
- edX: Fashion Design and Creation
Fashion Schools Worldwide
- Parsons School of Design (NYC)
- Fashion Institute of Technology (NYC)
- Central Saint Martins (London)
- London College of Fashion (London)
- Istituto Marangoni (Milan, Paris, London)
- Polimoda (Florence, Italy)
- Bunka Fashion College (Tokyo)
- RMIT University (Melbourne)
Fashion Blogs, Podcasts and YouTube Channels
Here are some fashion blogs on different fashion industry areas, podcasts that are usually a deep dive on the industry and some YouTube channels that talk about fashion history and some other industry secrets.
Blogs:
- Business of Fashion (BoF) – Covers fashion industry news, trends, and insights.
- The Impression – Focuses on runway shows, luxury fashion, and designer profiles.
- Style Not Com – An insider’s perspective on fashion and street style.
Podcasts:
- The Business of Fashion Podcast – Deep industry insights and interviews with designers and executives.
- Dressed: The History of Fashion – Explores fashion’s cultural and historical impact.
- The Cutting Room Floor – Unfiltered conversations with fashion insiders.
- Wardrobe Crisis – Sustainability-focused podcast hosted by Clare Press.
- Fashion Victims Podcast – Covers fashion scandals, trends, and industry news.
Channels:
- Bliss Foster – In-depth analysis of designer collections and fashion history.
- HauteLeMode – Fun, critical reviews of fashion shows and red carpet looks.
- Loic Prigent – Behind-the-scenes footage of top fashion houses.
- Mina Le – Explores historical and cultural influences in fashion.
Continue Reading:
How to Become a Fashion Designer? / Part 1
How to Become a Fashion Designer? / Part 2
How to Become a Fashion Designer? / Part 3
How to Become a Fashion Designer? / Part 4
How to Become a Fashion Designer? / Part 5
How to Become a Fashion Designer? / Part 6
How to Become a Fashion Designer? / Part 7
Written by Urtė Mikaitė



Add a Comment